Data Governance with Data Virtualization by Ali Aghatabar (Founder & Director) @ Intelicosmos®, Aug 21, 2021
[If you want to know more about Data Virtualization, you may want to reach out to my Data Virtualization blog first.]
In this article, I will explain how data governance is beautifully supported by Data Virtualization and Lyftrondata platform. Please check out below video for more information:
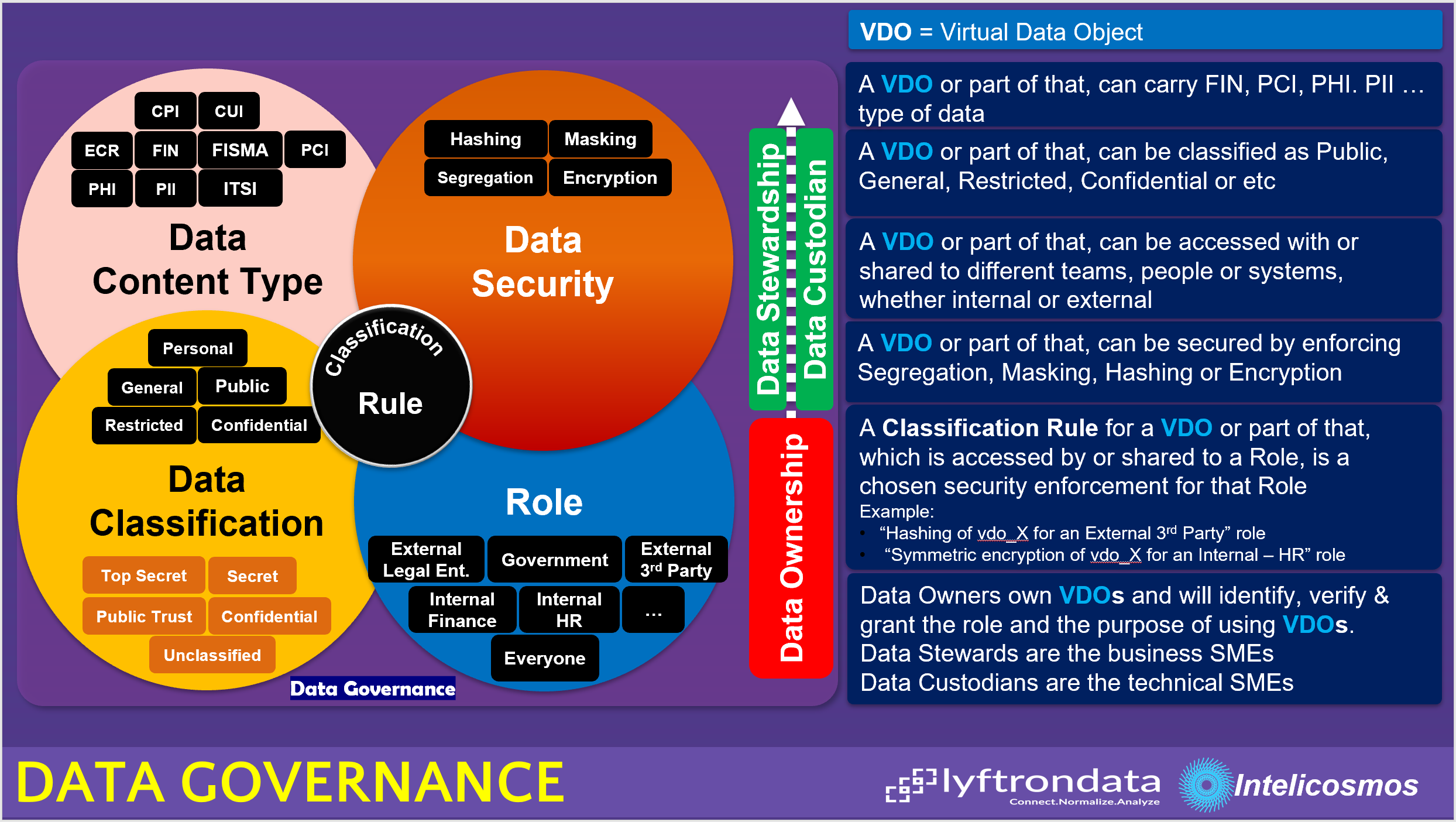
As you see in below picture, Data Governance is the process of identifying the nature of VDOs, understanding the purpose of using VDOs and pro-actively controlling and protecting VDOs while letting VDOs to be used by or shared to authorized people and systems. In Data Virtualization, VDOs are the centralized & virtual objects of all enterprise data assets, therefore, it is easy to view them all in one place, add, edit or review the metadata comes with VDOs, apply data governance rules and let VDOs to be used by or shared to consumers.
It starts with identifying what is the content of a VDO, what is the right classification level for that VDO (according to standards, laws etc), who is going to use it and therefore, what security mechanism must be applied to VDO, these steps are all supervised by Data Owners and supported by Data Stewards and Custodians.
In Data Virtualization all elements are virtual including connections, sources/targets, VDOs and their attributes, schemas and PIPEs. Data Governance and Data Sharing can be applied to any of these virtual items. So, Data Governance process is very flexible and change management cycle of that is very fast and simple. Lyftrondata gives us a centralized governance portal to easily apply governance rules, alter governance rules and monitor activities.
Let's look at Data Governance in more details. Data Governance has few important components and roles:
- Data Content Type: Explains the content of a VDO
- Data Classification: Explains the data classification levels according to the business type
- Role: It is about who is going to use a VDO or a VDO is shared to
- Data Security: Explains what security enforcement must be used to protect a VDO
- Data Owners: It is about people in an organization that own a VDO
- Data Stewards: It is about people in an organization that know a VDO from business process point of view
- Data Custodian: It is about people in an organization that know a VDO from technical point of view
Data Content Type
Data must be classified according to the content type. All VDOs are tabular form (of downstream structured, semi-structured or unstructured data) and content type can be referred to the whole VDO or individual attributes of that.
- CPI: Client Privileged Information
- CUI: Controlled Unclassified Information
- ECR: Export Controlled Research
- FIN: Financial Data
- FISMA: Federal Information Security Management Act
- ITSI: IT Security Information
- PCI: Payment Card Industry
- PHI: Protected Health Information
- PII: Personal Identifiable Information
- SIHSR: Sensitive Identifiable Human Subject Research
- ...
Data Classification
A Virtual Data Object (simply a VDO) can be classified to different levels but most commonly, VDOs are classified to ‘Personal, Public, General, Restricted and Confidential’ in non-government and 'Top Secret, Secret, Confidential, Sensitive, and Unclassified' in governments, but in-fact, your organization should be able to customize it based on your needs.
Non-government classes:
- Personal: Personal VDOs belong to individuals and must not be accessible by others unless with a permission of the individual itself. Family photo is an example that is not shared with public unless shared by individual itself.
- Public: There is no restriction in Public VDO and VDO can be freely available for anyone. As an example, company share price is a public information and classified as Public.
- General: This is the day-to-day company information that is not for public but is available for all staff. As an example, company next year strategy is classified as General.
- Restricted: Restricted VDO is highly sensitive, and its access must be limited known cases. Restricted VDO is commonly protected by an NDA (Non-disclosure Agreement). As an example, trade secrets are restricted information that when exposed unintentionally, may have significant financial or legal impact to the business
- Confidential: Confidential VDOs are business information which must be used inside business by authorized business units. One example is company pricing strategy that when exposed unintentionally, could negatively affect your business and ultimately your brand
- ...
Government classes:
- Top Secret: The highest security classification. "Top Secret shall be applied to information, the unauthorized disclosure of which reasonably could be expected to cause 'exceptionally grave damage' to the National Security that the original classification authority is able to identify or describe." It is believed that 1.4 million Americans have top secret clearances
- Secret: This is the second-highest classification. Information is classified Secret when its unauthorized disclosure would cause "serious damage" to national security. Most information that is classified is held at the secret sensitivity
- Confidential: This is the lowest classification level of information obtained by the government. It is defined as information that would "damage" national security if publicly disclosed, again, without the proper authorization
- Public Trust: Despite common misconception, a public trust position is not a security clearance, and is not the same as the confidential clearance. Certain positions which require access to sensitive information, but not information, which is classified, must obtain this designation through a background check. Public Trust Positions can either be moderate-risk or high-risk
- Unclassified: Unclassified is not technically a classification; this is the default and refers to information that can be released to individuals without a clearance. Information that is unclassified is sometimes restricted in its dissemination as Controlled Unclassified Information
- ...
Role
A Role in Lyftrondata, is essentially an individual account or a group of individual accounts and a Connection, a Source, a VDO or part of a VDO can be accessed by that Role. Access for a Role is called Access Right and different permissions can be granted or denied. VDO also is used or shared to someone or a Role in your organization or outside of your organization.
Below are some permissions that can be granted/denied with Access Right to a Role:
System Administration Rights / Alter / Alter Data Sources / Control / Control Data Sources / Create Schema / Create VDO / Delete / Insert / Select / Update / View Definition / ...Data Security Model
A VDO also can be secured from unauthorized accesses through different data security methods like Segregation, Masking, Hashing or Encryption:
- Segregation: Put your sensitive VDO into separate DataLake or separate virtual schema and let authorized people / systems only access it.
- Data Masking: Data Masking is a making part of data unreadable while some other parts are readable like hiding day and month of DatePaid but let year to be readable (cast(year([DatePaid]) as nvarchar(4)) + '-xx-xx’). Also, clearing data at all is another way of masking, means, no data would be available. It is a good approach for sensitive columns only.
- Hashing: Hashing of a data is a one-way encryption of that data, means it can’t be reverted to original data (HASHBYTES('SHA2_256', CreditCard)).
- Symmetric Encryption: Symmetric encryption is two ways encryption with same key, same as zipping a file with password and unzipping the file with the same password (EncryptByKey(‘A_SHARED_PASSWORD’, Amount)).
- Asymmetric Encryption: Asymmetric encryption is two ways encryption with public / private keys, means data is encrypted with Public Key and can be decrypted only by Private Key.
The key point is here. In order to protect a VDO but still be able to effectively use or share it for data, analytics or integration purposes, a VDO which is not in Public classification and is going to be used by a Role, must be protected with a proper security enforcement. This customized security enforcement is called Classification Rules.
As an example, you may want to ‘hash a restricted VDO when is shared with an external user’ but ‘symmetrically encrypt that restricted VDO when used by internal HR team’.
Data Ownership
In enterprises, Data Ownership is an important role that essentially owns the VDOs (like client banking transactions) and grants people/systems to use them.
Data Stewardship
Data Stewardship is also another role in enterprises that understands VDOs from business process point of view VDO and can help consumers to use them effectively.
Data Custodian
Like Data Stewardship is also another role in enterprises that understands VDOs from technical point of view VDO.
Lyftrondata Platform
Lyftrondata as a real Data Virtualization platform helps organizations to implement Data Governance at any level and all objects. Below is list of Data Governance features and objects in Lyftrondata that can be protected by Data Governance:
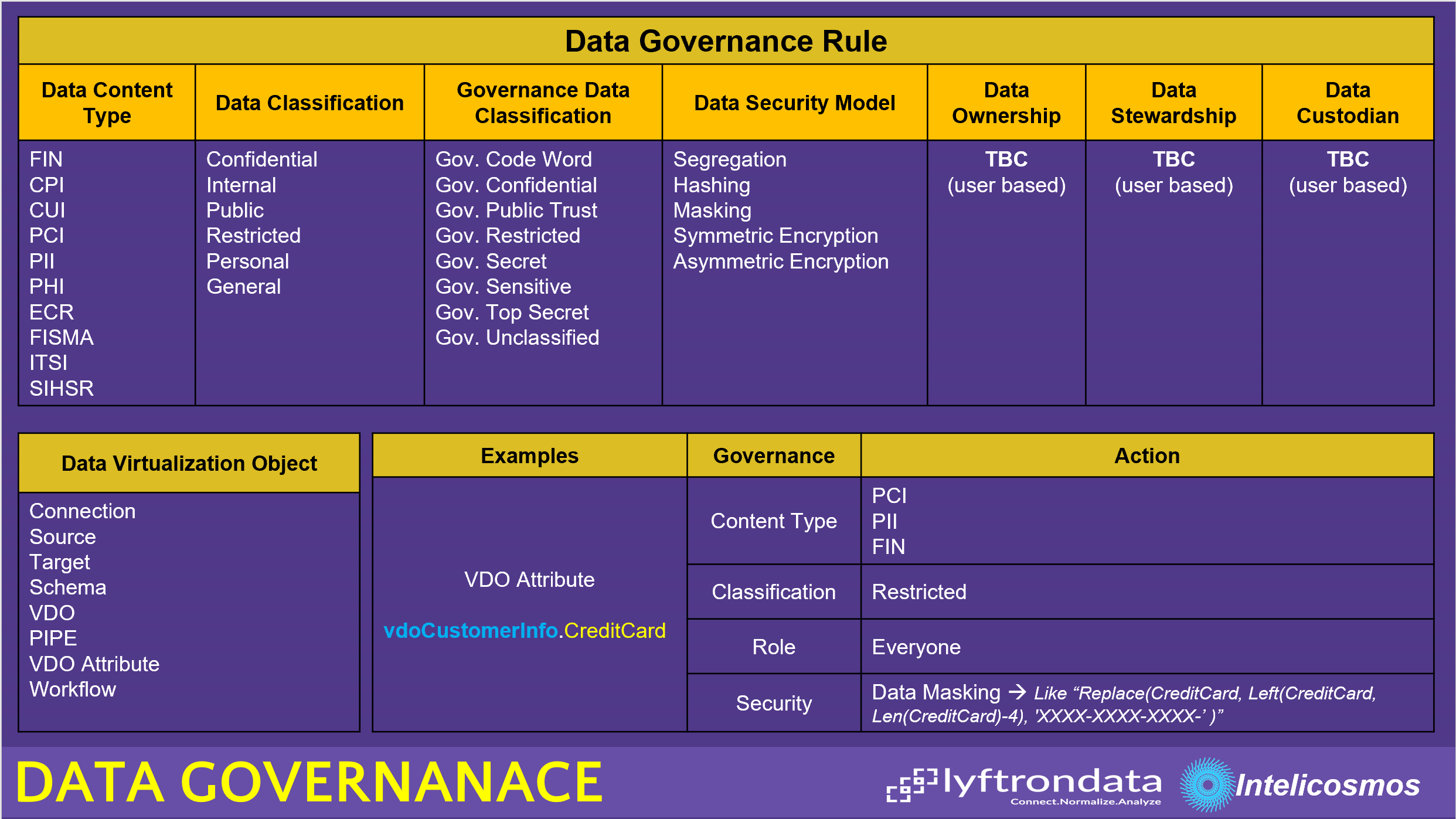
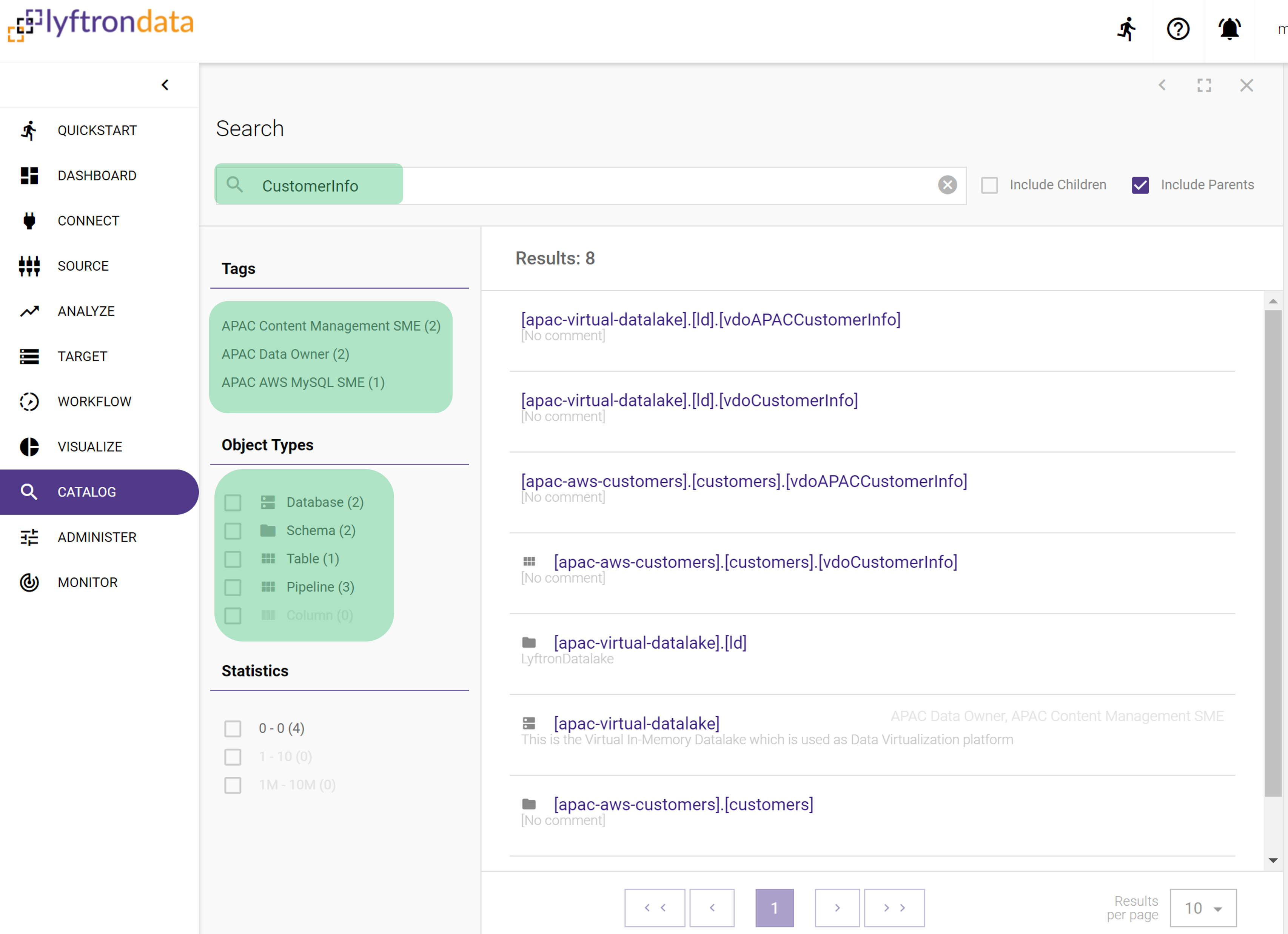
And here are some snapshots that explain how Data Governance is implemented in Lyftrondata platform:
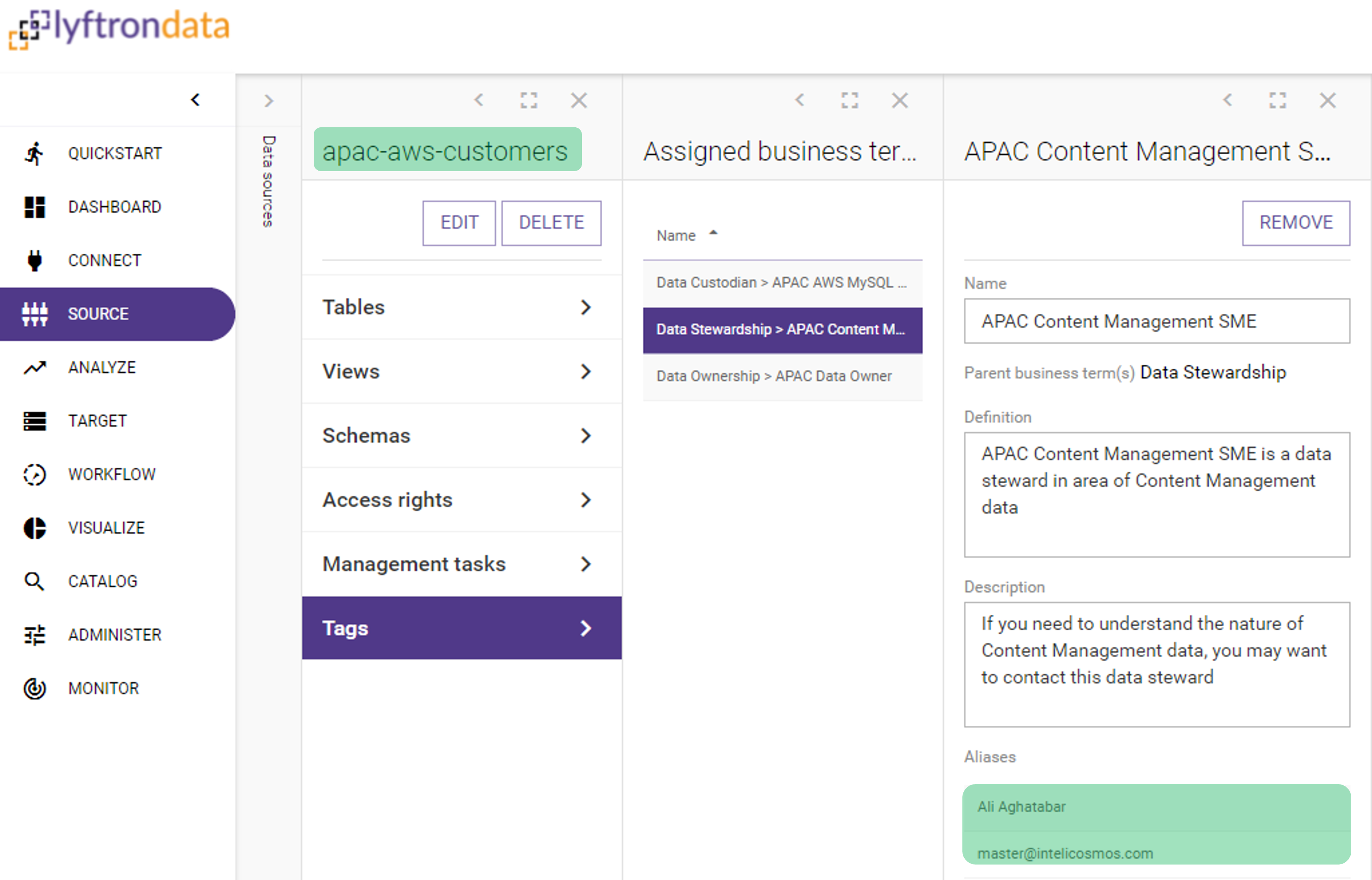
Example 1 - apac-aws-customers source:>
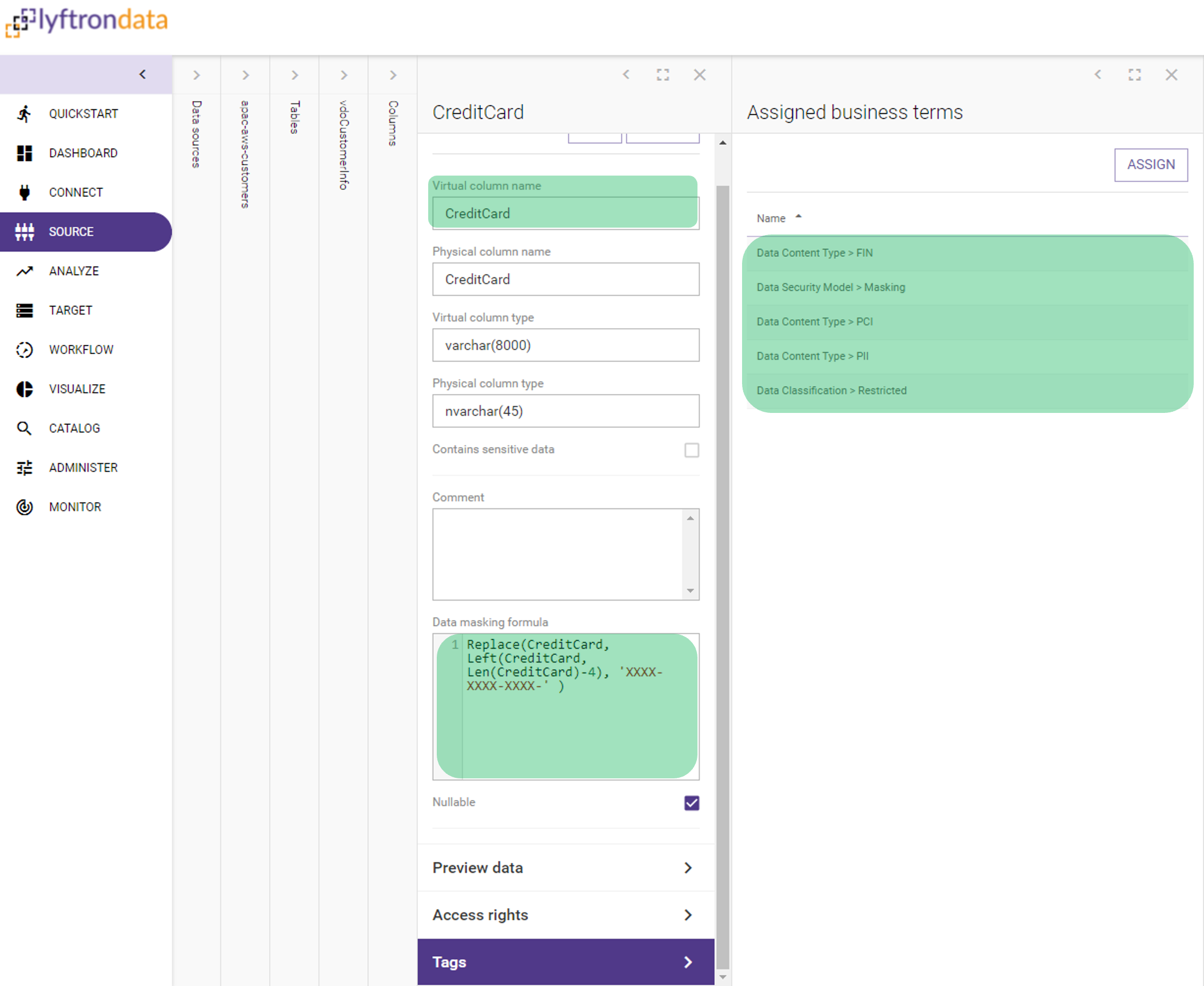
Example 2 - vdoCustomerInfo.CreditCard VDO:>
Example 3 - Data Dictionary:>

Ali Aghatabar, founder and director of Intelicosmos®, has been helping clients across the globe, particularly the APAC region, for over two decades. With a consulting background, he helped a wide range of clients and industries for their IT needs specially on data & analytic, cloud architecture and computing, AI and process automations, digital transformation, IoT and smart devices etc.
